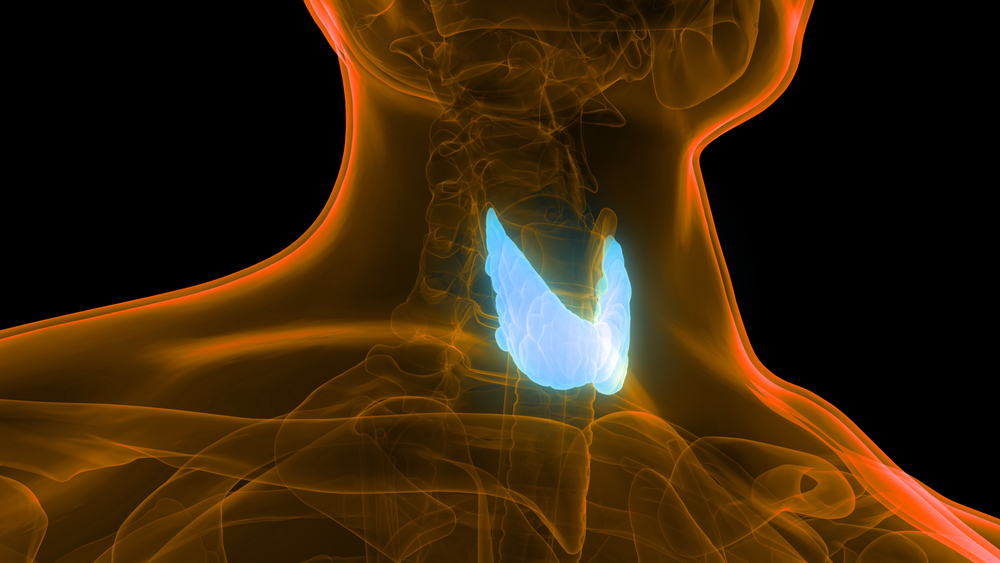
Introduction to the Thyroid Gland
Let’s embark on a journey to understand the thyroid gland, a vital part of our endocrine system. This butterfly-shaped gland, located in the lower front of the neck just below the Adam’s apple, is a powerhouse of hormone production.
Its physical description is as unique as its functions. It comprises two lobes connected by a thin piece of tissue known as the isthmus. This gland is small, typically weighing less than an ounce, but its role in the body’s metabolic activity is immense.
In the upcoming sections, we will delve deeper into the importance of the thyroid gland and why it matters for our overall health. Get ready to unlock the secrets of this small yet mighty gland!

The Essential Role of the Thyroid in the Body
The thyroid, a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck, plays a pivotal role in maintaining the body’s physiological balance through the production of hormones. Primarily, it generates triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), which regulate the body’s metabolism, an essential process for growth, development, and energy production.
These hormones don’t just stop at metabolism; they extend their influence to virtually every organ system in the body. From boosting heart rate, controlling body temperature, to assisting in protein synthesis, thyroid hormones are integral to overall health. A well-functioning thyroid ensures the body operates at an optimal pace, not too fast or too slow.
Thyroid Hormones and Their Widespread Impact
Thyroid hormones are crucial for body’s myriad functions. They contribute to brain development, bone health, and even menstrual cycle regularity in women. Additionally, they play a role in maintaining optimal cholesterol levels, thus indirectly promoting heart health. An imbalance in these hormones can lead to disorders like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, causing various symptoms and health issues.

Deep Dive into Thyroid Hormones
Your thyroid is a powerhouse that produces two vital hormones namely, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones play a crucial role in regulating your body’s metabolism, thereby influencing your energy levels, body temperature, and even your heart rate. (source)
Production and Release of Thyroid Hormones
The production and release of T4 and T3 are a complex process, primarily regulated by the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is produced by the pituitary gland located in your brain. When your body requires more energy, for instance during cold weather, TSH stimulates the thyroid to produce and release more T4 and T3. (source)

Iodine’s Role in Thyroid Hormone Production
Iodine is an essential trace mineral that your body cannot produce but requires for the production of T4 and T3. The thyroid cells are unique in that they absorb iodine to produce these hormones. A deficiency in iodine can lead to reduced thyroid hormone production, or hypothyroidism. It’s therefore crucial to maintain a diet that meets your daily iodine requirements. (source)

The Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis and its Role in Regulating Thyroid Hormone Production
The hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis is a complex interactive system that plays a vital role in regulating the body’s metabolism. The hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH then triggers the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones into the bloodstream. This is a closed-loop system, where the level of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream provides feedback to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, regulating further hormone production. [1]
How Disruptions in the HPT Axis Can Lead to Thyroid Disorders
Problems within the HPT axis can disrupt the delicate balance of hormone production, leading to thyroid disorders. For instance, an overactive or underactive hypothalamus or pituitary gland can result in excessive or insufficient TSH, causing hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, respectively. Similarly, issues within the thyroid gland itself, such as inflammation, can disrupt hormone production. Understanding this axis is key to diagnosing and treating thyroid-related health issues. [2]
For a comprehensive understanding of thyroid disorders, it’s important to delve into the HPT axis and its functioning. This knowledge aids healthcare professionals in providing effective treatments and guides patients towards better management of their conditions.
Common Thyroid Disorders: An Overview
Thyroid disorders often result from the thyroid gland producing either too much or too little thyroid hormone. These conditions, known as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can have significant impacts on your overall health.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is characterized by fatigue, weight gain, and depression due to the thyroid gland not producing enough thyroid hormone. Causes can range from autoimmune disease to certain medications. Treatment typically involves thyroid hormone replacement.

Hyperthyroidism
In contrast, hyperthyroidism presents with symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heart rate, and nervousness due to excess thyroid hormone. Causes can include Graves’ disease and thyroid nodules. Treatment often involves medication, radioactive iodine, or surgery.
Other Thyroid Disorders
Besides these, other thyroid disorders include thyroid nodules, goiter, thyroiditis, and thyroid cancer. Each comes with its unique set of symptoms, causes, and treatments.
Impact of Thyroid Disorders on Health
Thyroid disorders, specifically hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, have profound implications on your health. These conditions, which involve either an underactive (hypothyroidism) or overactive (hyperthyroidism) thyroid, can significantly affect physical health causing symptoms ranging from fatigue and weight changes to palpitations and increased sensitivity to temperature.
Thyroid Disorders and Mental Health
It’s not just your physical health that’s at risk. Thyroid disorders are also linked to mental health problems like depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment. The hormonal imbalance caused by these conditions can wreak havoc on your mental state, leading to significant emotional and cognitive disturbances.
Long-Term Consequences of Untreated Thyroid Disorders
When left untreated, thyroid disorders can lead to serious health problems such as cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and infertility. Therefore, it’s crucial to get an early diagnosis and treatment to prevent these long-term complications.
Why is Thyroid Health Essential?
The thyroid, a small gland located in your neck, plays a critical role in your body’s overall health and wellbeing. It regulates your metabolism, which is essential for numerous bodily functions, including heart rate and body temperature. Mayo Clinic explains that when your thyroid doesn’t function properly, it can lead to a host of health problems, such as obesity, heart disease, and infertility. Therefore, maintaining thyroid health is of utmost importance.
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle in Thyroid Health
Research indicates that diet and lifestyle can significantly impact your thyroid health. Consuming a balanced diet rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc can support thyroid function. Studies have also shown that stress can negatively affect your thyroid, emphasizing the importance of stress management and regular exercise.
Tips for Promoting Thyroid Health
- Regular Check-ups: Regular thyroid screening can help detect any abnormalities early, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients essential for thyroid function can help maintain its health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help regulate your metabolism and support your thyroid function.
- Stress Management: Activities like meditation and yoga can help manage stress levels, thereby supporting thyroid health.

Conclusion: The Significance of Thyroid Health
In our exploration of the thyroid gland and its critical role in the body, we’ve discovered that this small organ’s impact is anything but trivial. Involved in a diverse array of physiological processes, the thyroid regulates everything from metabolism to heart rate.
Understanding and maintaining thyroid health is therefore not just beneficial, but essential. A disruption in thyroid function can lead to various disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. It is crucial for us to take proactive steps in preserving our thyroid health and to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms of a thyroid disorder are suspected.
Thyroid health is a complex, multi-faceted topic, but armed with knowledge and awareness, we are all better equipped to support our own well-being. It’s never too late to start prioritizing your thyroid health.

Dr. Martha Pyron is a recognized sports medicine physician and the founder of Medicine in Motion, an Austin-based practice specializing in comprehensive medical care for active individuals and athletes. An active contributor to her field, she uses her extensive experience as a former collegiate athlete to aid her patients and develop innovative care strategies. Beyond her clinical practice, Dr. Pyron is known for her involvement in the local athletic community and her commitment to promoting health and fitness.